Large language models (LLMs) promise transformative capabilities: generating text, answering questions, summarising, translating, assisting with knowledge work, and more.
But for large enterprises building product solutions, the risks are real: misuse, bias, hallucination, privacy breaches, and safety failures.
Cohere, OpenAI, and AI21 Labs jointly published a set of preliminary best practices for deploying language models, aimed at guiding organisations to deploy responsibly and reliably.
In this post, we walk through those best practices from an enterprise lens: what they are, what they imply for you, and how to adopt them in real product and solution settings.
Core Best Practices (Summarised)
Below are the key recommended principles for deploying language models in a robust and responsible way.
Publish Use Guidelines & Terms of Use
Define clear usage policies and terms that prohibit misuse such as spam, fraud, misinformation, defamation, and illicit activity. Make expectations explicit to users.
Perform a Risk Assessment of Potential Harms
Before deployment, evaluate possible risks: both intentional misuse and unintentional harms such as bias, privacy leakage, or misleading outputs. Consider domain-specific threats.
Rigorous Evaluation Including Edge/Adversarial Cases
Test models not only with expected inputs but also with adversarial prompts, corner cases, and rare scenarios. Provoke failures, detect hallucinations, and assess robustness.
Transparency & Documentation
Publish documentation of model training, known limitations, failure modes, metrics, safety evaluations, and caveats. Be open about what the model can and cannot do.
User Controls, Monitoring & Feedback Loops
Monitor real usage, allow users to flag problematic outputs, collect feedback, and refine over time. Detect anomalies and enable rollback or refinement.
Privacy, Data Protection, and Security
Ensure input and output data is handled securely, anonymised where needed, and encrypted in transit and at rest. Be compliant with data protection regulations.
Bias Mitigation & Fairness
Actively test for model bias across demographics, user groups, and domains. Ensure that outputs don’t unfairly disadvantage or misrepresent specific groups.
Limiting Misuse & Abuse
Add guardrails, filters, and safety constraints to reduce the risk of harmful output such as hate speech, disinformation, or illegal content. Restrict high-risk usage where necessary.
Iterative Improvement & Fail-Safes
Recognise models are imperfect. Build in fail-safe mechanisms, human-in-the-loop checks, the ability to disable or revert features that misbehave, and the capacity to continuously update the model.
Collaboration & External Review
Engage with external stakeholders: researchers, domain experts, and impacted communities. Invite audits, peer review, and transparency in evaluation.
What These Practices Mean for Enterprises & Product Teams
To make the above principles actionable in enterprise settings, here is how to apply them in product development, deployment, and solution delivery.
Embed Safety & Governance Early
Treat safety, privacy, compliance, fairness, and auditability not as add-ons, but as core requirements in product specs. In your product lifecycle (planning, design, development, deployment), include checkpoints for risk, bias, security, and stakeholder review.
Build Observability & Metrics
Instrument your systems with logs, monitoring, and alerts for anomalous outputs, usage spikes, or content violations. Define metrics and KPIs such as error rates, outlier frequency, user complaints, hallucination frequency, and bias measures. Use dashboards to track model drift, performance degradation, and feedback trends.
Vendor & Model Provider Evaluation
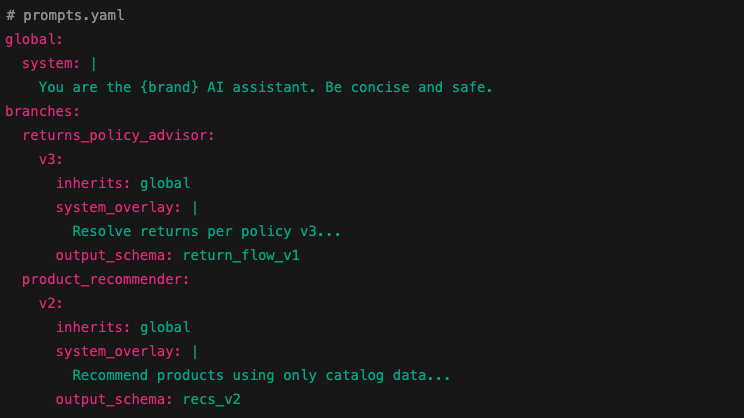
If using third-party or managed LLM providers, require them to supply documentation of training, safety evaluations, limitations, logs, and red-teaming reports. Require SLAs and contractual guarantees around content safety, fallback behaviour, data privacy, and the ability to disable problematic endpoints.
Domain / Use-Case Specific Testing
For your vertical (finance, legal, healthcare, manufacturing, etc.), test the model on domain-specific prompts, adversarial inputs, and corner cases. Bring in domain experts to validate outputs and spot subtle errors. Define acceptable failure modes: what is tolerable and what must be human-reviewed or blocked.
Human-In-The-Loop & Oversight
For higher-risk or mission-critical tasks, keep humans in the loop. Don’t rely entirely on automated outputs. Allow users or moderators to flag or override output, provide corrections, or request safe fallback. Use feedback to retrain or update the model and guardrails.
Update, Maintenance & Versioning
Plan regular updates, retraining, fine-tuning, or patching. Keep versioning of models so you can roll back if new versions degrade or misbehave. Maintain backward compatibility or migration paths so dependent systems don’t break.
Privacy & Data Controls
Ensure data handling meets legal and regulatory standards. Use data minimisation, anonymisation, or pseudonymisation where possible. Secure data in transit and at rest. Consider synthetic or proxy data for training or testing in sensitive domains.
Governance, Ethics & Stakeholder Engagement
Form an internal oversight committee including legal, compliance, security, and domain experts. Engage communities or end users for input on fairness, bias, and potential harms.
Consider external audits or third parties to review your LLM deployment. Be transparent with users about how the model works, its limitations, and how you mitigate risks.
Risks & Trade-Offs to Be Aware Of
When applying best practices, enterprises should also recognise the inherent trade-offs and limitations:
Performance vs Safety: stronger guardrails or filters may reduce fluency, creativity, or utility of outputs.
Cost & Complexity: monitoring, retraining, safety infrastructure, human review, and audits add cost and engineering overhead.
Evolving Threats: Adversarial misuse evolves; what is safe today may not be tomorrow.
Opaque Failures: diagnosing root causes of incorrect outputs can be non-trivial.
Liability & Legal Risk: harmful or biased outputs may expose enterprises to legal or reputational risk.
Vendor Dependency & Auditability: with third-party models, you may have limited visibility into model internals.
How Accelerai Embeds These Practices in Client Solutions
At Accelerai, when we partner with large enterprises to build AI-powered solutions, we embed these best practices as foundational pillars, not optional extras.
From initial scoping with AI Consultants, we define safety, compliance, fairness, and auditability as non-negotiable architectural goals.
We implement observability, logging, anomaly detection, and feedback loops in all deployments.
We conduct domain-specific adversarial testing and validation with client SMEs.
We build human-in-the-loop oversight paths and fallback mechanisms for critical use cases.
We manage versioning, rollback, and update strategies to ensure continuity and safety.
We help clients evaluate and select LLM providers, demand transparency and guarantees, and structure contracts accordingly.
We assist with governance, stakeholder review, and external audits or third-party checks.
Get in touch today to see how we can help your business build AI powered solutions.